Surveying in Civil Engineering: Objectives, Principles, Classification & Uses
What is Surveying in Civil Engineering?
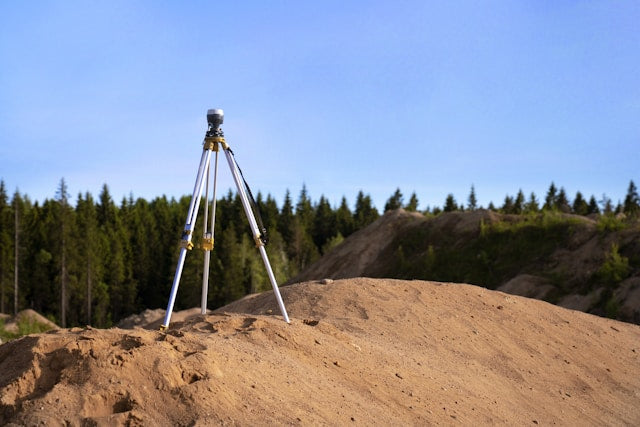
Surveying is an important civil engineering activity in which measurements and mapping of the area of land is performed to ascertain relative position of points and distance between points. It forms the backbone of construction project planning and designing since it provides the precise spatial data for planning engineering and infrastructure.

Surveying is basically the science and the art of positioning points in the earth or in three dimensions in the right position, along with the angles between the points and the distance between them. This information is required for the preparation of accurate map, drawings, and blueprints which are the foundations for civil engineering works such as the construction of buildings, roads, bridges, and other structures.
By accurate measurement and mapping of the area, the surveyor can acquire valuable data about the topography, features, or structures present at the site. The data is later used by civil engineers in planning and designing the projects in line with the particular features of the site, in order to ensure maximum efficiency, performance, and safety.
Why is Surveying Important for Civil Engineering Projects?
Surveying is of paramount importance in civil engineering work for a number of important reasons. First and foremost, it establishes the targets and benchmarks according to which the whole project is regulated. The main aims of surveying are to establish the relative positions of the objects accurately, measure the dimensions and angles correctly, and make accurate maps or plans of the construction area.

There are two principles which are considered to be the basic in surveying procedures: working from whole to part, and measuring the positions of points with reference to points known. By abiding by these principles, surveyors can provide for the consistency and precision of measurements, which is integral to the effective planning and designing of the work of construction. In addition, surveying produces the accurate spatial data necessary for effective planning and design of infrastructures. Civil engineers utilize such data in designing structures which are not only effective as well as secure, but also best placed in the environment. It would be very hard to plan and execute extensive construction projects in an effective manner in the absence of precise data obtained through surveying.
Surveying becomes necessary at the planning and designing stage of the construction work too. By mapping the surface of the land and identifying the probable hurdles or difficulties in the process, the surveyors let the civil engineers design the plan in accordance with the specifications of the region. This helps in keeping the future structure balanced in its stability as well as in providing for its effective usage of the resources along with minimizing the risk of delays or complexities in the construction work.
How is Surveying Classified?
Surveying can be classified into different categories based on several factors:
Classification Based on Nature
-
Land Surveying: This type of surveying is carried out on land and is the most common form. It involves measuring and mapping the topography, boundaries, and features of land areas.
-
Marine Surveying: Also known as hydrographic surveying, this type is conducted in water bodies such as oceans, lakes, and rivers. It is used to measure and map the depth, topography, and other features of underwater areas.
-
Underground Surveying: This type of surveying is performed in underground structures like mines, tunnels, and caves. It helps in mapping and planning the layout of these underground structures.
-
Aerial Surveying: This involves surveying from the air using aircraft or drones. It is useful for mapping large areas quickly and efficiently.
Classification Based on Object
-
Engineering Surveying: This type of surveying is used for planning, designing, and constructing various engineering projects, such as buildings, roads, bridges, and dams.
-
Military Surveying: This form of surveying is used for military purposes, such as mapping terrain, planning operations, and locating strategic positions.
-
Geological Surveying: This type of surveying is used to study and map the Earth's surface and subsurface features, such as rock formations, mineral deposits, and geological structures.
Classification Based on Instruments Used
-
GPS Surveying: This method uses Global Positioning System (GPS) technology to determine precise locations and elevations on the Earth's surface.
-
Total Station Surveying: Total stations are advanced electronic/optical instruments that combine theodolites (for measuring angles) and EDM (Electronic Distance Measurement) devices for highly accurate surveying.
-
Laser Scanning Surveying: This technique uses laser scanners to capture detailed 3D point cloud data of objects, structures, and landscapes.
-
Photogrammetric Surveying: This method involves taking aerial or ground-based photographs and using specialized software to extract spatial data and create maps or 3D models.
The classification of surveying techniques helps surveyors choose the most appropriate method based on the specific requirements, terrain, and desired outcomes of a project.
Applications of Surveying in Civil Engineering
Surveying is significant in several civil engineering applications. Among the most significant applications is the planning of construction projects, in which surveying data is central to the design as well as the execution of the construction projects such as roads, bridges, buildings, and dams. The surveyors measure the ground and map it, providing accurate data about the topography, elevations, and structures present, which becomes the foundation for architectural as well as engineering plans.

Another significant application of surveying is the determination of boundaries. Surveys locate the lines of properties, ensuring construction projects remain in legal bounds and avoid intruding onto other properties. This is particularly important in areas of high population density, in which properties are minimal in size, with boundary lines often complex.
Surveying is also essential in transferring the map details to the actual ground. After the design and the plans have been made, the surveyors use their skills in transferring the map details onto the actual ground correctly. This entails the establishment of reference points, control networks, and guiding the construction team in the exact implementation of the project as indicated in the plan.
In addition to construction, surveying is also used in navigation, mainly in maritime and aviation. Precise surveying information is needed in the production of nautical charts, in providing safe passage for boats and planes, and in the detection of any dangers or hindrances.
Survey techniques are used in archaeology to map, document historical sites, ruins, and artifacts. Archaeologists work in association with surveyors to create extensive surveys and models for the preservation of significant details of ancient cultures as well as ancient structures.
In most applications, civil engineering applications of surveying are diverse and integral. Ranging from construction planning and boundary surveys to archaeology surveys, surveying provides the critical spatial knowledge and measurement to ensure accurate and successful project implementation in various fields.
Modern Surveying Techniques and Technologies
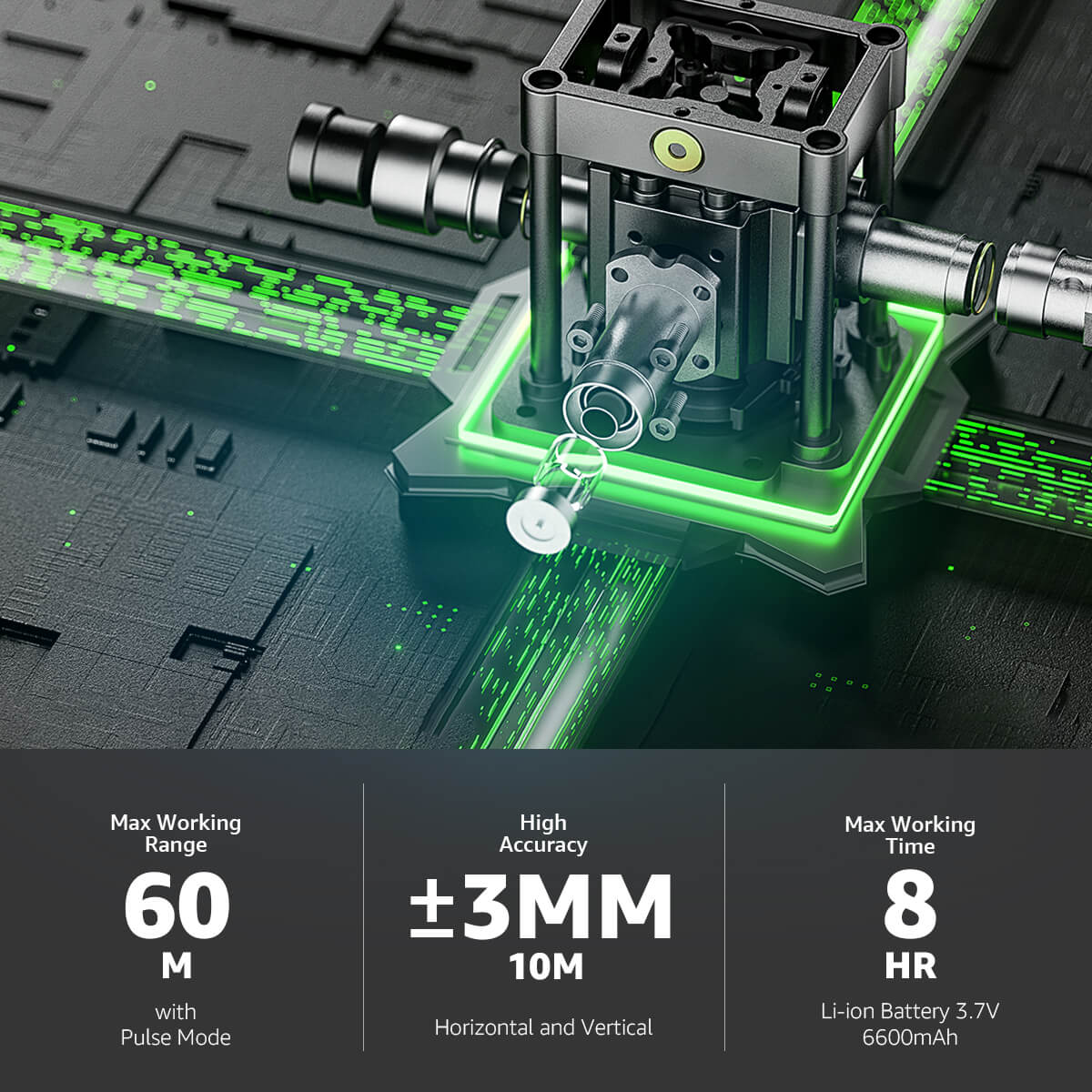
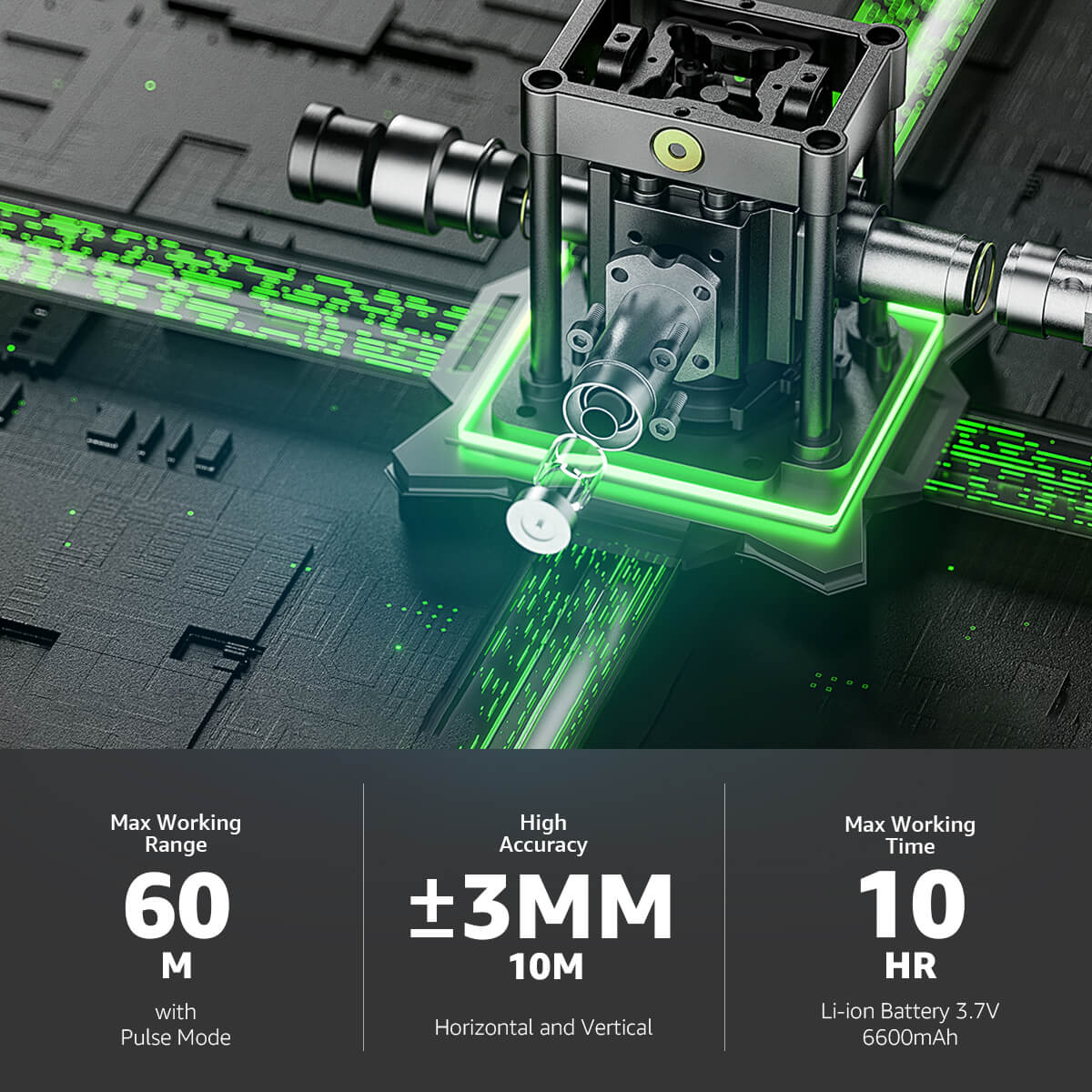
Modern technological advancements have revolutionized the field of surveying by embracing enhanced and more effective ways of collecting spatial data. There are three new surveying techniques which have revolutionized civil engineering projects: the Global Positioning System (GPS), the total station, and the Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM) tool.
GPS technology has proven itself to be a great tool for surveyors, with the ability to determine the coordinates of any Earth surface point with precision. A network of satellites orbiting the Earth allows the position of a GPS receiver to be determined by triangulation, receiving very accurate position data. The procedure for surveying is made easier by the use of GPS technology, eliminating the time-consuming measurements at scale and significantly reducing the time and budget required for extensive projects.
Total stations, on the other hand, have electronic theodolites (angle measuring instruments) incorporated into them along with EDM instruments (distance measuring instruments) in one single piece of equipment. Multi-function instruments, the total stations can measure horizontal angles, vertical angles, and distance quickly with very accurate results. Total stations are the standard for the majority of survey work, replacing the older, slower, error-prone techniques.
EDM stands for Electronic Distance Meters, which use laser or infrared technology to record distance accurately. By emitting electromagnetic waves, which are received by the device, the device determines the object distance with minimal margin of error. The distance measurement in surveying is made much easier with the use of EDM instruments by providing accurate information for long-range measurement as well as in adverse conditions. The convergence of the emerging technologies has not only heightened the level of productivity and precision in survey work but also extended the limits of possibility. The greater degree of confidence with which surveyors can now approach bigger and more complex projects is the outcome of the immense quantity of precise data obtained through the use of GPS, total stations, and EDM instruments. Plotting out vast landscapes or creating complex infrastructures, these new techniques have been a boon of immense benefit to the profession of civil engineering.